Blog Post
Unraveling the Enigmatic Interleukin-39: A Novel Player in Immune Regulation
Interleukin-39 (IL-39) has emerged as a captivating cytokine with unique immunomodulatory properties, influencing diverse aspects of immune function and inflammation. In this blog post, we delve into the fascinating world of IL-39, exploring its discovery, functions, and potential implications in health and disease.
Discovery of Interleukin-39
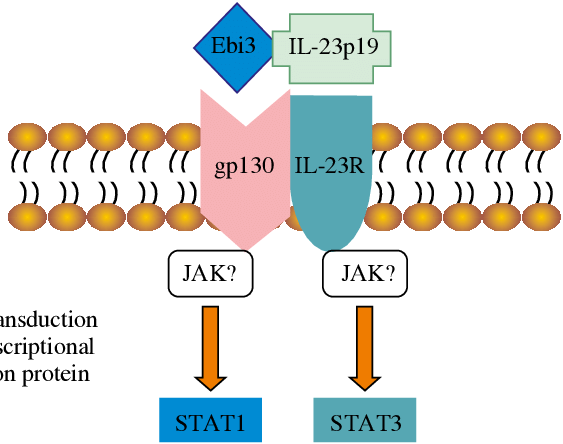
IL-39 belongs to the IL-12 cytokine family but stands out for its distinct heterodimeric structure, comprising the IL-23 receptor (IL-23R) and the p19 subunit of IL-23. This unconventional composition grants IL-39 a specialized role in immune regulation, differentiating it from other cytokines within the IL-12 family.
Functions and Mechanisms
The key functions of IL-39 encompass:
- Immune Cell Activation: IL-39 stimulates the activation and proliferation of various immune cells, including T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells, thereby enhancing immune responses against pathogens and tumors.
- Inflammatory Modulation: IL-39 contributes to the regulation of inflammatory processes by promoting the production of proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), influencing the balance between inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signals.
- Autoimmune Regulation: IL-39 exhibits dual roles in autoimmune diseases, acting as both a proinflammatory mediator and a regulator of immune tolerance. Its precise effects depend on the specific context and microenvironment within tissues.
- Tissue Homeostasis: Emerging evidence suggests that IL-39 plays a role in tissue repair and regeneration, contributing to tissue homeostasis and wound healing processes.
Implications in Health and Disease
The dysregulation of IL-39 has been implicated in various immune-related disorders and conditions, including:
- Autoimmune Diseases: IL-39’s involvement in autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) underscores its significance in immune dysregulation and autoimmunity.
- Infectious Diseases: IL-39’s ability to enhance immune responses against infections highlights its potential in combating microbial pathogens and supporting host defense mechanisms.
- Cancer Immunity: IL-39’s impact on immune cell activation and anti-tumor immune responses suggests a role in cancer immunotherapy strategies, warranting further exploration in the context of tumor microenvironments.
Therapeutic Potential and Future Directions
The therapeutic implications of IL-39 are still under investigation, with potential avenues including:
- Targeted Immunotherapy: Modulating IL-39 signaling pathways or targeting IL-39-associated immune responses may offer novel therapeutic strategies for immune-mediated disorders and cancer.
- Precision Medicine: Understanding IL-39’s role in immune regulation and disease pathogenesis can inform personalized treatment approaches, tailoring interventions based on individual immune profiles.
- Biologics Development: Biologic agents targeting IL-39 or its receptors are being explored for their potential in modulating immune function and inflammation, with implications for precision medicine and immune-targeted therapies.
Conclusion
Interleukin-39 represents a promising frontier in immunology, contributing to our understanding of immune regulation, inflammation, and disease pathogenesis. As research progresses, unlocking the full potential of IL-39 may pave the way for innovative therapies and precision immunomodulatory interventions across various health conditions.