Blog Post
Unraveling the Significance of Interleukin-32 (IL-32) in Immune Regulation
Introduction Interleukin-32 (IL-32) has emerged as a key player in immune regulation, impacting various aspects of immune responses and inflammatory pathways. In this blog post, we delve into the multifaceted roles of IL-32, its cellular interactions, and its implications in health and disease.
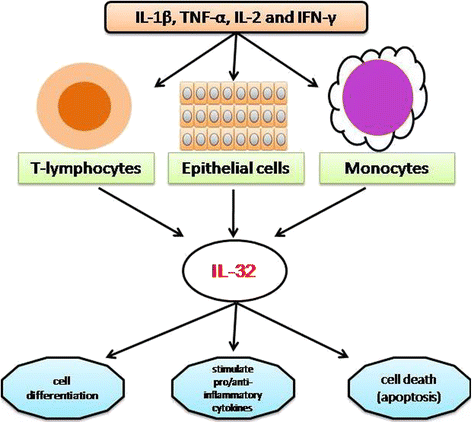
Exploring Interleukin-32 (IL-32) IL-32, initially discovered as a pro-inflammatory cytokine, is now recognized for its diverse functions beyond inflammation. It is produced by various cell types, including immune cells, and exerts its effects through multiple signaling pathways.
Key Functions of IL-32
- Immune Modulation: IL-32 influences immune cell activation, differentiation, and cytokine production, contributing to the regulation of both innate and adaptive immune responses.
- Inflammatory Responses: IL-32 plays a role in inflammatory processes, promoting the release of pro-inflammatory mediators and modulating immune cell behaviors in the context of infection, autoimmunity, and cancer.
- Cellular Interactions: IL-32 interacts with different cell types, such as macrophages, T cells, and epithelial cells, influencing their function and contributing to the complexity of immune signaling networks.
Clinical Implications and Disease Associations
- Infectious Diseases: IL-32’s involvement in immune responses makes it relevant in infectious diseases, including viral infections, bacterial infections, and inflammatory responses to pathogens.
- Autoimmune Disorders: IL-32 dysregulation has been linked to autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and psoriasis, highlighting its role in autoimmune pathogenesis.
- Cancer Immunity: IL-32’s effects on immune cell function and tumor microenvironment suggest potential implications in cancer immunity, with ongoing research exploring its role in anti-tumor responses and immunotherapy strategies.
Therapeutic Potential and Future Directions Understanding IL-32’s intricate roles opens avenues for therapeutic interventions, including targeted immunomodulatory approaches, cytokine-based therapies, and precision medicine strategies in immune-related disorders.
Conclusion Interleukin-32 (IL-32) serves as a dynamic regulator of immune responses, inflammation, and cellular interactions, impacting diverse aspects of immune system function. Unraveling IL-32’s complexities enhances our knowledge of immune regulation and offers insights into therapeutic innovations for immune-mediated diseases.