Blog Post
Deciphering the Role of Interleukin-31 (IL-31) in Inflammatory Pathways
Introduction Interleukin-31 (IL-31) stands at the intersection of immunology and inflammation, playing a crucial role in various inflammatory conditions. In this blog post, we unravel the complexities of IL-31 signaling, its impact on immune responses, and its relevance in inflammatory diseases.
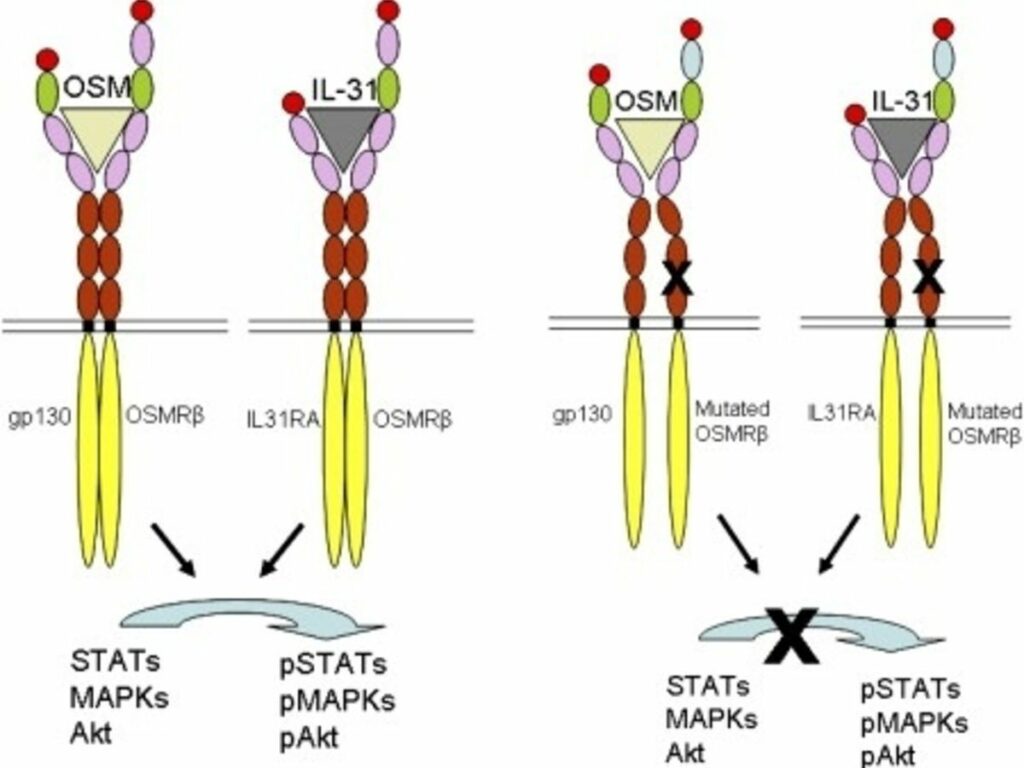
Understanding Interleukin-31 (IL-31) IL-31 belongs to the IL-6 cytokine family and is primarily produced by activated T cells, especially TH2 cells. It exerts its effects through the IL-31 receptor, influencing immune cells and contributing to inflammatory processes.
Key Functions of IL-31
- Pruritus and Dermatitis: IL-31 is strongly associated with pruritus (itching) and dermatitis, playing a role in inflammatory skin conditions such as atopic dermatitis, prurigo nodularis, and allergic contact dermatitis.
- Inflammatory Responses: IL-31 contributes to inflammatory responses by promoting cytokine production, immune cell activation, and tissue damage, particularly in the skin and mucosal tissues.
- Neuroimmune Interactions: IL-31 has effects on the nervous system, influencing neuronal activity and contributing to the sensation of itching, highlighting its neuroimmune crosstalk.
Clinical Implications of IL-31
- Skin Disorders: IL-31’s involvement in pruritus and dermatitis makes it a target for therapeutic interventions in skin disorders, with ongoing research focusing on IL-31 inhibitors and modulators.
- Allergic Inflammation: IL-31 contributes to allergic inflammation, linking it to conditions like allergic rhinitis, asthma, and other allergic responses mediated by TH2 immune pathways.
- Chronic Inflammatory Conditions: IL-31’s pro-inflammatory effects extend to chronic inflammatory diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriasis, where it contributes to disease progression and symptoms.
Therapeutic Targeting of IL-31 Research efforts are underway to develop IL-31-targeted therapies, including antibodies against IL-31 or its receptor, small molecule inhibitors, and biologics aimed at modulating IL-31 signaling pathways.
Future Directions and Research Insights Advancements in understanding IL-31 biology pave the way for novel treatment strategies, precision medicine approaches, and potential biomarkers for monitoring inflammatory diseases associated with IL-31 dysregulation.
Conclusion Interleukin-31 (IL-31) emerges as a pivotal player in inflammatory pathways, particularly in skin disorders, allergic inflammation, and chronic inflammatory conditions. Exploring IL-31’s intricate roles offers new avenues for targeted therapies and improved management of inflammatory diseases.