Blog Post
Interferon Beta: Unraveling its Impact on the Immune System
Introduction: Interferon beta (IFN-β) stands as a pivotal player in the complex orchestra of the immune system. This cytokine, part of the interferon family, has garnered significant attention due to its multifaceted roles in immunomodulation, antiviral defense, and potential therapeutic applications. Understanding the historical journey and diverse functions of IFN-β unveils its intriguing story in the realm of immunology.
History and Discovery: Discovered in the early stages of interferon research, IFN-β emerged as a distinct type I interferon. Its identification marked a breakthrough in understanding the body’s response to viral infections. Initially recognized for its potent antiviral properties, subsequent research shed light on its broader immunomodulatory effects. The journey of IFN-β from discovery to a deeper understanding of its mechanisms showcases the relentless pursuit of knowledge in immunological research.
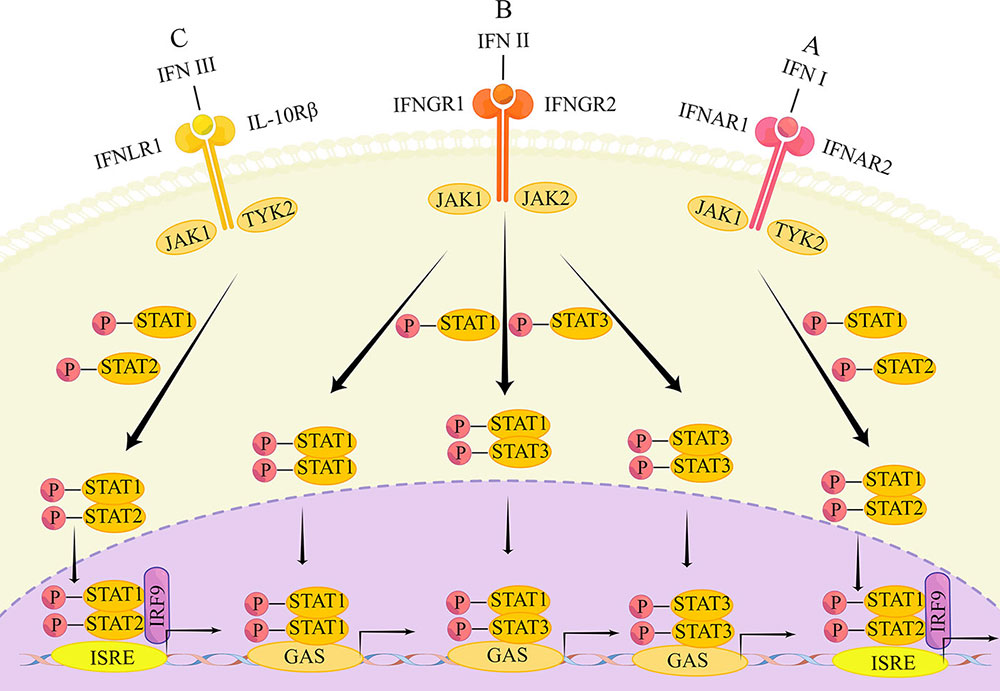
Roles in Immunology: IFN-β operates at the intersection of innate and adaptive immunity. One of its primary functions is the activation of various immune cells, including macrophages and natural killer (NK) cells. This activation, in turn, enhances the host’s ability to combat viral infections. Beyond antiviral defense, IFN-β plays a crucial role in regulating the inflammatory response, contributing to the delicate balance required for immune homeostasis.
Therapeutic Applications: The unique immunomodulatory properties of IFN-β haven’t gone unnoticed in the medical field. Therapeutically, it has been harnessed for conditions such as multiple sclerosis (MS), where its ability to regulate the immune system has shown promise. By modulating the inflammatory processes associated with autoimmune diseases, IFN-β has become a cornerstone in the treatment landscape.
Conclusion: In summary, interferon beta’s journey from its discovery to its current standing as a key immunomodulatory cytokine is a testament to the ever-evolving landscape of immunology. Its historical significance, coupled with its diverse roles in immunomodulation and therapeutic applications, positions IFN-β as a captivating subject in the ongoing exploration of the immune system.