Blog Post
Understanding the Cell Cycle: A Comprehensive Guide
The cell cycle is the series of events that a cell undergoes as it grows and divides, producing two daughter cells. It is a complex process that is essential for all life.
Interphase
During interphase, the cell grows and prepares for DNA replication. It then enters the S phase, where the cell replicates its DNA. Finally, the cell enters the G2 phase, where it prepares for mitosis by synthesizing proteins and other molecules needed for cell division.
Mitosis
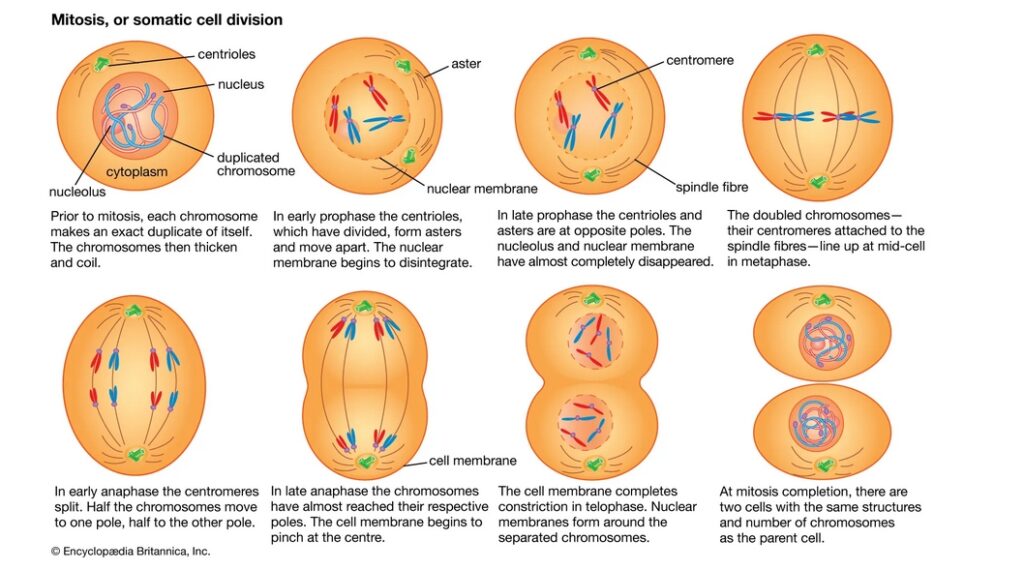
Mitosis is the process by which the nucleus of a cell divides into two daughter nuclei. It is divided into four main sub-phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- Prophase: In prophase, the chromosomes condense and the spindle apparatus forms.
- Metaphase: During metaphase, the chromosomes align in the center of the cell.
- Anaphase: During anaphase, the sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase: In telophase, the nuclear envelope reforms around the two sets of chromosomes.
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm into two daughter cells. It typically occurs simultaneously with the later stages of mitosis.
G0
G0 is a resting phase of the cell cycle. Cells that are not actively dividing or differentiating may enter G0.
Regulation of the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is tightly regulated by a number of checkpoints. These checkpoints ensure that the cell has completed all of the necessary steps in one phase before proceeding to the next. If any errors are detected at a checkpoint, the cell cycle will be paused or halted until the errors are corrected.
Importance of the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is essential for all life. It allows cells to grow, divide, and produce new cells. This is necessary for growth, repair, and reproduction.
Conclusion
The cell cycle is a complex and fascinating process that is essential for all life. By understanding the cell cycle, we can better understand how cells grow, divide, and develop. This knowledge can be used to develop new treatments for diseases and to improve our understanding of human biology.

